- Barajar
ActivarDesactivar
- Alphabetizar
ActivarDesactivar
- Frente Primero
ActivarDesactivar
- Ambos lados
ActivarDesactivar
- Leer
ActivarDesactivar
Leyendo...
Cómo estudiar sus tarjetas
Teclas de Derecha/Izquierda: Navegar entre tarjetas.tecla derechatecla izquierda
Teclas Arriba/Abajo: Colvea la carta entre frente y dorso.tecla abajotecla arriba
Tecla H: Muestra pista (3er lado).tecla h
Tecla N: Lea el texto en voz.tecla n
![]()
Boton play
![]()
Boton play
![]()
31 Cartas en este set
- Frente
- Atrás
- 3er lado (pista)
|
Human resources main goals
|

|
|
|
HR tasks field
|

1. Preparation of the work place:
- personnel planning - personnel recruitment (one of the most important tasks and the manager should do the interviews for hiring new employees) 2. Work performance: - personnel performance - personnel management (also important) - personnel appraisal - personnel reward - personnel development (also important) 3. Personnel exemption: - personnel layoff (Appraisal: is a method by which the job performance of an employee is documented and evaluated. Consists of regular reviews of employee performance within an organization.) |

3
|
|
HR definition
|

HRM:
Responsibility of those who manage people. Involves: 1. Planning for human resources needs 2. Including recruitment and selection 3. Training and development 4. Promotion and transfer 5. Redundancy and retirement 6. Welfare and safety 7. Wage and salary administration 8. Collective bargaining 9. Most of industrial relations |
PRTPR
WWCM |
|
HR objectives
|

Economic goals 5
- optimal assignment of employees - optimal integration of work - profitability - enhancement of human work performance - usage of creativity PROFIT + EFFICIENCY social goals 6 - scope of work - work place design - occupational safety - management - motivation - participative management BALANCE $ & PEOPLE SUPERIOR GOAL: harmonious relationship between objectives of the company and the interest of the employees |
|
|
History HR
|

1. Institutionalization:
- 1965 personnel management was created - most relevant factor was the organization and the structure - personnel had to adapt to the complex companies requirements 2. Humanization: - 1970 influence came from USA - consideration of person with feelings, needs, and values - satisfaction of employees was the final goal and more money was inn vested in this field 3. Economization: - 1980 personnel and organization requirements had to adapt to the market conditions -strategy had to lead to rationalization of the development potential --> efficiency 4. Entrepreneurship - 1990 HR becomes an essential factor in the company - not only an employee but a member of the company - new challenges in the globalization world: client orientation, information, technologies - horizontal integration of activities and units of a company |

|
|
Personnel planning principles and issues
|

Planning:
Decision on qualitative and quantitative personnel demand needed. Constant protection of production factor labor. Optimal assignment of employment through knowledge of job requirements Creation of best possible working conditions Principles: 5 - Labour market - flexibility and personal commitment - personnel adjustment - diversity - human dignity Issues: 3 - dependence of other business plans - high degree of uncertainty: human factor. People get sick, can quit, can get pregnant, can have an accident - high numbers of conditions to be considered: personnel structure, individual agreement, laws, collective wage agreements, personnel planning in media sector. |
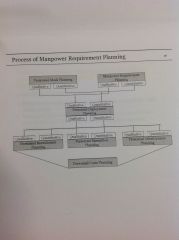
|
|
Personnel recruitment classification
Process Supply channel |

Def: providing the necessary manpower for the company in qualitative, quantitative and geographical terms.
|
|
|
Job description
Profile Requirements |

|
|
|
Job description
Profile Requirements |

|
|
|
Selection methods
|

|

|
|
Job description
Profile Requirements |

|
|
|
Selection methods
|

|

|
|
General competence model
|

|
|
|
Personnel placement definition
Job enlargement |

|
|
|
HR development definition and types
|

|
|
|
HR development definition and types
|

|
|
|
Importance of HR development for...
Types of mobility |

|
|
|
Employee apparaisal
Definition Objectives Types |

|
|
|
Personnel management and motivation
Definition Goal Type of motivation instruments |

|
|
|
Job evaluation
Definition Goal Methods |

|
|
|
Job evaluation
Definition Goal Methods |

|
|
|
Personnel reward
Definition Structure |

|
|
|
Personnel layoff definition
|

|
|
|
Personnel layoff types
|

|
|
|
Personnel portfolio
|

|
|
|
Aspects of HR
|
1. Process control:
- supervising the behavior of employees - interactional and structural behavior control 2. System design - establishment of rules and conditions that should be followed in order to regulate the supervision of behavior and directly influence the behavior of employees. |
|
|
HR Strategy types
|
1. Independent functioning
Corporate strategy and HRM function independently. In this case is very difficult to organize the company because the two things are not closely connected. 2. HRM derives from CS This is the normal situation for a company.from the corporate strategy you can decided which kind of people the company needs. 3. CS derives from HRM: You have a kind of employees and according to that you create a proper strategy for a company. 4. Integrative approach: Is the best one because the HRM strategy is incorporated in the company strategy. Everything should function in a simultaneous way. |
4
|
|
Pestel framework explanation
|
Macro environmental factors that can influence the HRM management and the strategic management
Political Economical Social Technological Environmental Legal Similar to SWOT Strength Weakness Opportunities Threats |

|
|
Theory of X and Y manager
|
X manager:
Attitude against the employment. Negative attitude that caused that employees dislike their work. People was forced to work almost with threat of punishment. It is a way of managing that beliefs that employees prefer to be directed and need a strong leader, and avoid responsibility. Employees are not motivated. Y manager: Motivated employees where they are able to have self control, they are motivated and want to take responsibilities. It is a democratic Leadership style, participative and cooperative. |
|
|
Challenges of HR
|
- demographic factors
- recruiting talents - work life balance - globalization - change of values - diversity - digitalization (requires training) |
|
|
What can be done when the qualifications overpass the requirements?
|
1. Job enrichment: to assign higher quality of tasks. Is an attempt to motivate employees by giving the opportunity of using the range of their abilities. "Vertical loading" of work.
2. Job enlargement: is the assignment of additional tasks of the same level of complexity. The quantity of tasks grow without changing the challenge. Is an "horizontal loading" of work 3. Job rotation: regular and systematic changing of jobs and tasks within the employees of the company. |
3
|