- Barajar
ActivarDesactivar
- Alphabetizar
ActivarDesactivar
- Frente Primero
ActivarDesactivar
- Ambos lados
ActivarDesactivar
- Leer
ActivarDesactivar
Leyendo...
Cómo estudiar sus tarjetas
Teclas de Derecha/Izquierda: Navegar entre tarjetas.tecla derechatecla izquierda
Teclas Arriba/Abajo: Colvea la carta entre frente y dorso.tecla abajotecla arriba
Tecla H: Muestra pista (3er lado).tecla h
Tecla N: Lea el texto en voz.tecla n
![]()
Boton play
![]()
Boton play
![]()
4 Cartas en este set
- Frente
- Atrás
|
Empiricism
|
Knowledge acquired through senses.
This branch was born in England under the strong influence of Isaac Newton. The only way to know the world is through empiric experience (your senses! lol). There can't be innate ideas. |
|
John Locke
|
Knowledge is originated by the senses; without these, our mind is like a "tabula rasa".
The thinking process goes from sensorial perceptions to Simple Ideas to Reflection (or Complex) ideas (combination of simple ideas). Primary qualities are in the objects (ex: solidity, extension, figure, mobility). They can be perceived through two or more senses. Secondary qualities are the product of the influence of objects in our senses (ex. textures, colors, sounds, tastes). They can only be perceived through one single sense. |
|
George Berkeley
|
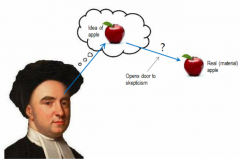
Primary and secondary qualities are both in the subject.
Distinguishes between sensations (reality) and sensorial objects (hypothetical). If the physical world exists, is only because God "creates it constantly". |
|
David Hume
|

Knowledge comes from perceptions, which leave sensorial impressions from which we form ideas.
Knowledge can be about facts and their relations or association of ideas. Concepts such as mind or God fall apart. Logical principles, such as cause and effect, are product of people's imagination. Man cannot know the real nature of the world: skepticism. This is because there can be relations of ideas (they tell us nothing about the world); or matters of fact (they're uncertain). |