- Barajar
ActivarDesactivar
- Alphabetizar
ActivarDesactivar
- Frente Primero
ActivarDesactivar
- Ambos lados
ActivarDesactivar
- Leer
ActivarDesactivar
Leyendo...
Cómo estudiar sus tarjetas
Teclas de Derecha/Izquierda: Navegar entre tarjetas.tecla derechatecla izquierda
Teclas Arriba/Abajo: Colvea la carta entre frente y dorso.tecla abajotecla arriba
Tecla H: Muestra pista (3er lado).tecla h
Tecla N: Lea el texto en voz.tecla n
![]()
Boton play
![]()
Boton play
![]()
39 Cartas en este set
- Frente
- Atrás
- 3er lado (pista)
|
(HTML Introduction) What is HTML?
|
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
|
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages - HTML describes the structure of a Web page - HTML consists of a series of elements - HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content - HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc. |
|
(HTML Introduction) A Simple HTML Document. Example.
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head> <title>Page Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>My First Heading</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> </body> </html> |

|
|
(HTML Introduction) Example explained:
|
1. The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document
|
2. The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page.
|
|
(HTML Introduction) 3. The <head> element contains meta information about the HTML page
|
4. he <title> element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab)
|
5. The <body> element defines the document's body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
|
|
(HTML Introduction) 6. The <h1> element defines a large heading
|
7. The <p> element defines a paragraph
|
|
|
(HTML Introduction) What is an HTML Element?
|
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
|
<tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>
|
|
(HTML Introduction) The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
|
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p> |

|
|
(HTML Introduction) What are empty elements?
|
Some HTML elements have no content (like the <br> element). These elements are called empty elements.
|
Empty elements do not have an end tag!
|
|
(HTML Introduction) What is the purpose of a web browser?
|
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
|
|
|
(HTML Introduction) Does a browser display the HTML tags?
|
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
|

|
|
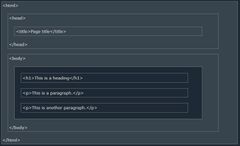
(HTML Introduction) HTML Page Structure
|
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
|
|
|
(HTML Introduction) Note:
|
The content inside the <body> section (the white area above) will be displayed in a browser.
|
The content inside the <title> element will be shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab.
|
|
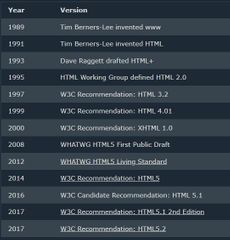
(HTML Introduction) (HTML History) Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML:
|
|
This tutorial follows the latest HTML5 standard.
|
|
(HTML Editors) A simple text editor is all you need to learn HTML.
|
Web pages can be created and modified by using professional HTML editors.
However, for learning HTML we recommend a simple text editor like Notepad (PC) or TextEdit (Mac). |
We believe in that using a simple text editor is a good way to learn HTML.
|
|
(HTML Editors) Follow the steps below to create your first web page with Notepad or TextEdit.
|
Step 1: Open Notepad (PC)
Windows 8 or later: Open the Start Screen (the window symbol at the bottom left on your screen). Type Notepad. Windows 7 or earlier: Open Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad |
|
|
(HTML Editors) Step 2: Write Some HTML.
Write or copy the following HTML code into Notepad: |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <body> <h1>My First Heading</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> </body> </html> |
|
|
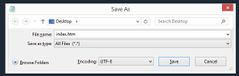
(HTML Editors) Step 3: Save the HTML Page. Save the file on your computer. Select File > Save as in the Notepad menu.
|
Name the file "index.htm" and set the encoding to UTF-8 (which is the preferred encoding for HTML files).
|
|
|
(HTML Editors) Tip:
|
You can use either .htm or .html as file extension. There is no difference, it is up to you.
|
|
|
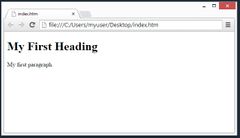
(HTML Editors) Step 4: View the HTML Page in Your Browser.
|
Open the saved HTML file in your favorite browser (double click on the file, or right-click - and choose "Open with").
The result will look much like this |
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) In this chapter we will show some basic HTML examples.
|
Don't worry if we use tags you have not learned about yet.
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Documents) All HTML documents must start with a document type declaration: __
|
All HTML documents must start with a document type declaration: <!DOCTYPE html>.
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Documents) How does the HTML document itself begin and end?
|
The HTML document itself begins with <html> and ends with </html>.
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Documents) The visible part of the HTML document is between ___.
|
The visible part of the HTML document is between <body> and </body>.
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Documents) Example:
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <body> <h1>My First Heading</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> </body> </html> |

|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration) What is the <!DOCTYPE> declaration?
|
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration represents the document type, and helps browsers to display web pages correctly.
|
It must only appear once, at the top of the page (before any HTML tags).
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration) The <!DOCTYPE> declaration is not case sensitive.
|
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration for HTML5 is
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Headings) How HTML headings are defined?
|
HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
|
<h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading.
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Headings) Example
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <body> <h1>This is heading 1</h1> <h2>This is heading 2</h2> <h3>This is heading 3</h3> <h4>This is heading 4</h4> <h5>This is heading 5</h5> <h6>This is heading 6</h6> </body> </html> |

|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Headings) How HTML paragraphs are defined?
|
HTML paragraphs are defined with the <p> tag.
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Headings) Example
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
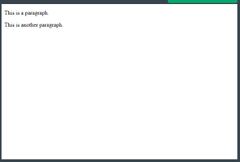
<html> <body> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p>This is another paragraph.</p> </body> </html> |
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Links) How HTML links are defined?
|
HTML links are defined with the <a> tag:
|
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Links) How HTML links are defined? (Example)
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <body> <h2>HTML Links</h2> <p>HTML links are defined with the a tag:</p> <a href="https://www.w3schools.com">This is a link</a> </body> </html> |

|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Links) The link's destination is specified in the href attribute.
|
Attributes are used to provide additional information about HTML elements.
|
You will learn more about attributes in a later chapter.
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Images) How HTML images are defined?
|
HTML images are defined with the <img> tag.
|
The source file (src), alternative text (alt), width, and height are provided as attributes.
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (HTML Images) Example
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <body> <h2>HTML Images</h2> <p>HTML images are defined with the img tag:</p> <img src="w3schools.jpg" alt="W3Schools.com" width="104" height="142"> </body> </html> |

|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) (How to View HTML Source?) View HTML Source Code:
|
Right-click in an HTML page and select "View Page Source" (in Chrome) or "View Source" (in Edge), or similar in other browsers.
|
This will open a window containing the HTML source code of the page.
|
|
(HTML Basic Examples) Inspect an HTML Element:
|
Right-click on an element (or a blank area), and choose "Inspect" or "Inspect Element" to see what elements are made up of (you will see both the HTML and the CSS).
|
You can also edit the HTML or CSS on-the-fly in the Elements or Styles panel that opens.
|
|
(HTML Elements) How an HTML element is defined?
|
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag.
|
|
|
(HTML Elements) What is an element?
|
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
|
<tagname>Content goes here...</tagname>
|