- Barajar
ActivarDesactivar
- Alphabetizar
ActivarDesactivar
- Frente Primero
ActivarDesactivar
- Ambos lados
ActivarDesactivar
- Leer
ActivarDesactivar
Leyendo...
Cómo estudiar sus tarjetas
Teclas de Derecha/Izquierda: Navegar entre tarjetas.tecla derechatecla izquierda
Teclas Arriba/Abajo: Colvea la carta entre frente y dorso.tecla abajotecla arriba
Tecla H: Muestra pista (3er lado).tecla h
Tecla N: Lea el texto en voz.tecla n
![]()
Boton play
![]()
Boton play
![]()
52 Cartas en este set
- Frente
- Atrás
- 3er lado (pista)
|
Biomolecules
|
Molecules that make up living things six common elements making up them ( c,H,O,N,S,P)
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Cn H2nOn also known as polydroxiketones
They help to conserve arterial pressure and provide energy for the body |
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
More than then monomers
|
|
|
Glyceraldehydo
|
3 carbons
|
|
|
Ribose
|
5 carbons
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Six carbons
|
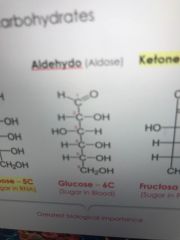
|
|
Fructosa
|
Six carbons
|
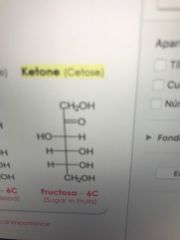
|
|
Saccaharose
|
Glucose+fructose
|
|
|
Saccaharose
|
Glucose+fructose
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Sugar vegetal origin used by living
|
|
|
Saccaharose
|
Glucose+fructose
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Sugar vegetal origin used by living
|
|
|
Fructose
|
Sugar found in fruits and honey
|
|
|
Saccaharose
|
Glucose+fructose
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Sugar vegetal origin used by living
|
|
|
Fructose
|
Sugar found in fruits and honey
|
|
|
Galactose
|
Animal origin sugar that when bonded with glucose forms lactose
|
|
|
Saccaharose
|
Glucose+fructose
|
|
|
Glucose
|
Sugar vegetal origin used by living
|
|
|
Fructose
|
Sugar found in fruits and honey
|
|
|
Galactose
|
Animal origin sugar that when bonded with glucose forms lactose
|
|
|
Maltose
|
Disaccharides present in malt and other grains, also in beer
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Among their main functions we can find:
Thermal isolation Organ protection Energy reserve and hormones |
|
|
Proteins
|
The union of aminoácids and Pepedic bond
|
|
|
Stereoscopic microscopic
|
Animal dissection, colony observation, parasite detection
|
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum
|
Membrane where protein synthesis occurs and maturation occurs
|
|
|
Golgi apparatus
|
Proteins a packed for distribution inside or outside the cell
|
|
|
Vacuoles
|
Stores water and temporary storage of disposal substances
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
Contain different digestive enzymes for degrading cellular material
|
|
|
Centrioles
|
Paired organelles that serve as force centers for cell division
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Power source for the cell providing energy
|
|
|
Chloroplasts
|
Contain chlorophyll and makes photosynthesis
|
|
|
Cilia
|
Locomotion feeding and cleaning
|
|
|
Flagella
|
Projections for locomotion and feeding
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
All chemical reactions happening inside the cell
|
|
|
Hook thought about monk cells
Anton van Leeuwenhoek |
Main discovers of the cell
|
|
|
Enzymes
|
Biocatalizers that accelerate chemical reactions in living beings
|
|
|
ATP
|
Adenosine triphosphate
|
|
|
Passive transport
|
Simple difussion
Osomosis Facilitated diffusion Do not requires energy |
|
|
Active transport
|
Endocitosis
Exocitosis Requires energy |
|
|
Catabolism
|
Energy is freed from the braking of molecules into smaller ones
|
|
|
Anabolism
|
Use free energy to build larger molecules from small ones
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Three stages glucosis ciclo de Krebs and electrones transport or oxidative
|
|
|
Fermentation
|
uses food production like cheese yogurt, ICE Cream
|
|
|
Prokaryotic cells
|
Cellular membrane, no nucleus, small and simpler, bacterias
|
|
|
Eukaryotic cells
|
Cellular membrane, big and complex,
|
|
|
Cell wall
|
Rigid barriers that gives protection to the cell
|
|
|
Citoplasm
|
Semi fluid material contained by the cell membrane
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton
|
Skeleton of the cell provides structure and compressibility
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
Control center of the cell
|
|
|
Nuclear membrane
|
Isolated the nucleus
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Organelle where protein synthesis occurs
|