- Barajar
ActivarDesactivar
- Alphabetizar
ActivarDesactivar
- Frente Primero
ActivarDesactivar
- Ambos lados
ActivarDesactivar
- Leer
ActivarDesactivar
Leyendo...
Cómo estudiar sus tarjetas
Teclas de Derecha/Izquierda: Navegar entre tarjetas.tecla derechatecla izquierda
Teclas Arriba/Abajo: Colvea la carta entre frente y dorso.tecla abajotecla arriba
Tecla H: Muestra pista (3er lado).tecla h
Tecla N: Lea el texto en voz.tecla n
![]()
Boton play
![]()
Boton play
![]()
23 Cartas en este set
- Frente
- Atrás
- 3er lado (pista)
|
Media Economics
|
Analyzing the economic relationships within the media market and media companies.
|
Economic+med market and comp.
|
|
Can do three types of Analysis
|
1. Macro Economics
2. Micro Economics 3. Also Business Administration |
MA E
MI E BA |
|
Macro Economics
|
Examining macroeconomic issues, such as labor and capital markets, policy and regulatory concerns etc.
|
LABOR
CAPITAL MARKETS POLICY REGULATORY |
|
Micro Economics
|
Examining microeconomic issues, such as media competition and concentration, market structure, ownership structure, financial performance of media companies etc.
|
MEDIA
–> COMPETITION –>CONCENTRATION –>MARKET –>OWNERSHIP –>FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE |
|
Business Administration
|
Focusing on a single company´s structure etc
|
ONE ENTERPRISE
|
|
Business Economics
|
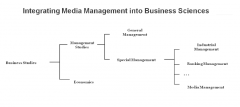
1. Business Management Process Engineering
2. General Business Administratrion 3. Special Busiess Administration |
3 Sections
|
|
1. Business Management Process Engineering
|
Secondary methods and procedures are provided for business economics
|
e.g.
ACCOUNTING COST ACCOUNTING BUSINESS STATISTICS |
|
2. General Business Administration
|
Examining sector–independent issues presenting functional and cross–sector relationships in order to promote inter–disciplinary thinking and decision making
|
Connection among departaments?
|
|
3. Special Business Administration
|
Analyzing the characteristics of a distinct set of enterprises, focusing on selected issues that are relevant only to certain companies or business units
|
Set Enterprises, focusing on issues relevant to them
|
|
Theoretical and terminological context
|
Media Economics and Media management
|
2 important concepts
|
|
Media Economics
|
The study of how media industries use scarce resources to produce content that is distributed among consumers in a society to satisfy various wants and needs
|
Media economics: media industries, scarce resources, produce, satisfy
|
|
Media Management
|
Consists of the ability to supervise and motivate employees and the ability to operate facilities and resources in a cost-effective manner
|
Media management: ability to supervise, operate facilities, cost effective
|
|
Purpose of economics
|
SO: forming theories and models which serve to explain phenomena observed in practica.
OO: Deriving recommendations for practice. |
Scientific objectiv and Operational objective
|
|
Basic questions
|
What should be produced?
And which benefits/services does the product provide? How should the services be provided? For whom should the services be provided? |
WHAT
HOW FOR WHOM |
|
Structure of Economic Transformation Processes
|
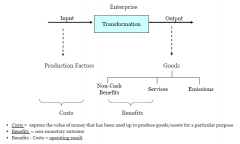
|
|
|
Production Factors
|
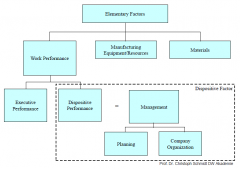
|
4
|
|
Explanation of Production Factors
|
WP: All performane provided by people in the company
R: Material and equipment used for producing the good, not part of the final product. M: Raw materials and supplies, and semi finished products incorporated to the final product and also used for the equipment. DF: Part of the WP factor, used for process of leading, directing, planning and organizing. |
WP: People
R: Equipment M: Raw materials DF: Soft skills |
|
Economic principle
|
Generally, economics is about achieving an optimum cost-effect relation due to the conflict between unlimited human needs and scarce resources. MR and ME.
|
MR: given input, maximum output
ME: given output, minimal input |
|
How important is competition?
|
Fundamental decision-making constraint, factors that influence the sustainability of firm profits.
|
Market entry conditions, market power of input suppliers, mp of product buyers, etc.
|
|
Defining Business Objectives
|
To have in mind:
Commercial media companies Non profit media companies Material and formal goals |
Categorizing media companies
Goals |
|
Targets
|
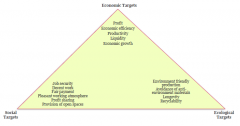
|
|
|
Basic mechanism of price formation
|
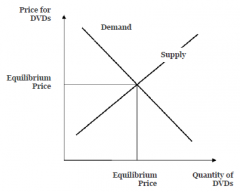
Demand: quantity of goods that consumer are willing to buy at a given price.
Supply: amount of good that producers are willing and able to sell at a given price. |
Demand and supply Market based regulation, price serves as indicator of scarcity of traded goodd and thus encourages to adjust.
|
|
Why should journalist deal with economics?
|
They should, because they work in companies that are guided by the economical principles, which is the profit maximization
|
Companies with Economic principle
|